November 2018 Issue
ISSN 2689-291X
ISSN 2689-291X
CORONARY ANGIOGRAPY
Basic Views
Introduction
Coronary arteriography remains the gold standard for identifying the presence and/or severity of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease, aiding decision–making with regards to appropriateness of coronary interventions [1]. It involves the selective injection of a radiopaque contrast agent directly into a coronary artery.
Coronary angiography has undergone major transformation ever since its inception by Dr. F. Mason Sones Jr. in 1959 [2]. Currently there are a variety of approaches utilizing multiple safer catheters and more convenient access sites, such as the radial approach, allowing earlier recovery and discharge with a lower incidence of vascular complications.
Patient evaluation with regards to suitability of cardiac catheterization, in addition to the skill and knowledge of the basic techniques of vascular access, catheter advancement and coronary engagement remain the cornerstone for the performance of a safe coronary angiogram [3]. These are beyond the scope of this review; we will concentrate on interpretation of the basic angiographic views.
References:
Coronary arteriography remains the gold standard for identifying the presence and/or severity of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease, aiding decision–making with regards to appropriateness of coronary interventions [1]. It involves the selective injection of a radiopaque contrast agent directly into a coronary artery.
Coronary angiography has undergone major transformation ever since its inception by Dr. F. Mason Sones Jr. in 1959 [2]. Currently there are a variety of approaches utilizing multiple safer catheters and more convenient access sites, such as the radial approach, allowing earlier recovery and discharge with a lower incidence of vascular complications.
Patient evaluation with regards to suitability of cardiac catheterization, in addition to the skill and knowledge of the basic techniques of vascular access, catheter advancement and coronary engagement remain the cornerstone for the performance of a safe coronary angiogram [3]. These are beyond the scope of this review; we will concentrate on interpretation of the basic angiographic views.
References:
- Di Mario C, Sutaria N. Coronary angiography in the angioplasty era: projections with a meaning. Heart. 2005 Jul;91(7):968-76.
- Loop FD. Classics in thoracic surgery. F. Mason Sones, Jr., (1918-1985). Ann Thorac Surg. 1987 Feb;43(2):237-8.
- Kosova E, Ricciardi M. Cardiac Catheterization. JAMA. 2017 Jun 13;317(22):2344.
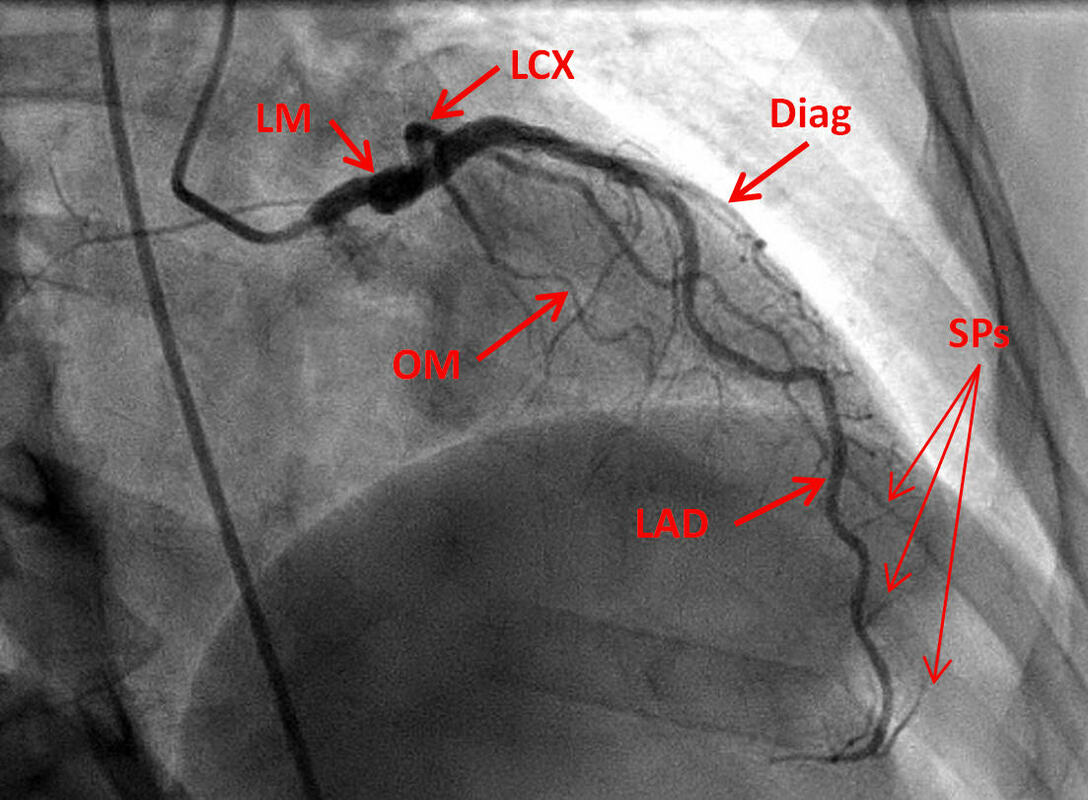
LEFT CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY
RAO Caudal
AP Caudal
LAO Caudal (Spider View)
LAO Cranial
AP Cranial
RAO Cranial
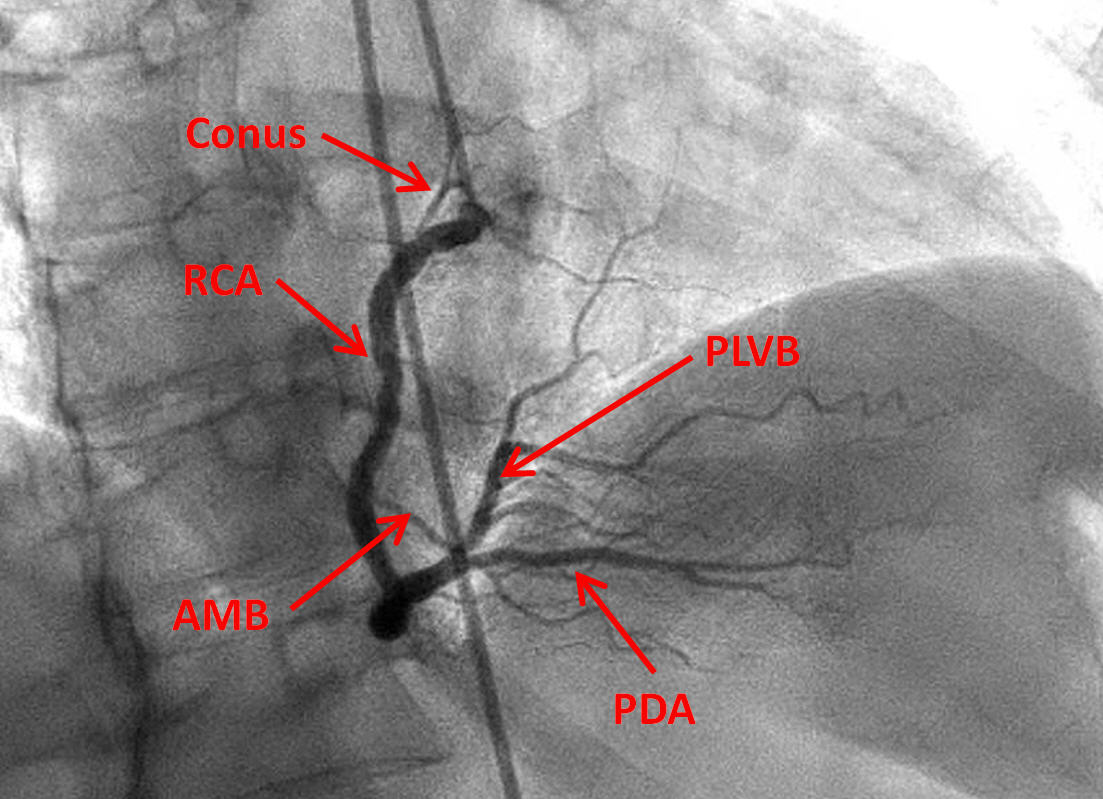
RIGHT CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY
LAO Straight
LAO - AP Cranial
RAO Straight
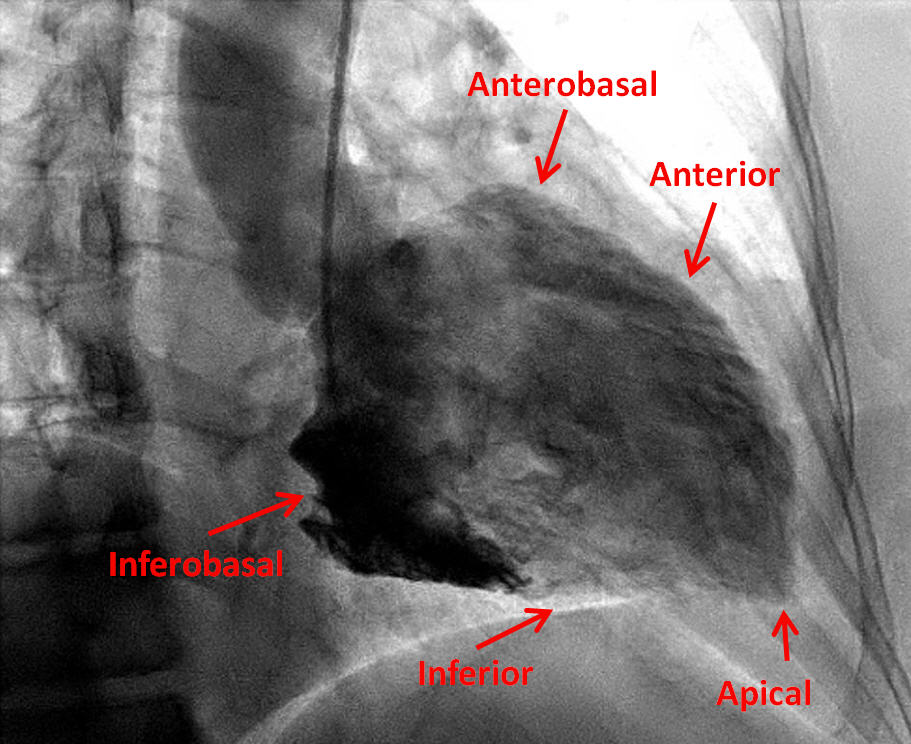
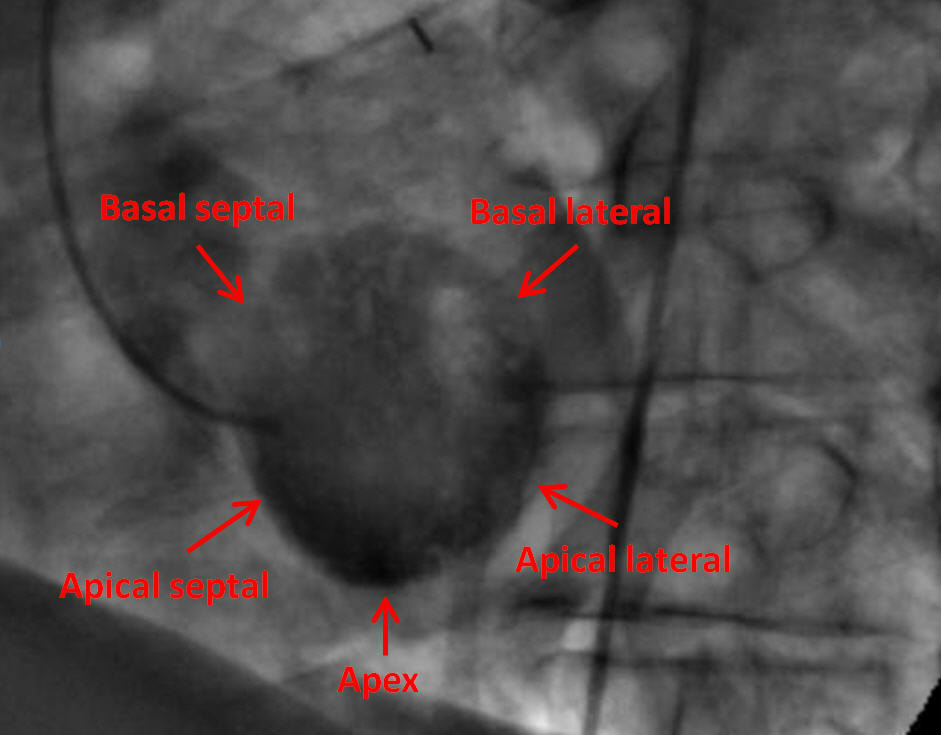
LEFT VENTRICULOGRAPHY
LV Gram (RAO Cranial)
LV Gram (LAO Cranial)
Test You Knowledge
Allow popups in google chrome and press on box below to start flash quiz
| Coronary Angiography Practice Quiz (Download) |
Authors:
Sarina Sachdev, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Bassam Omar, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
G. Mustafa Awan, M.D.
Associate Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
George Eyrich, M.D.
Adjunct Professor of Cardiology
Diagnostic and Medical Clinic
Mobile, AL
Sarina Sachdev, M.D.
Cardiology Fellow
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Bassam Omar, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
G. Mustafa Awan, M.D.
Associate Professor of Cardiology
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
George Eyrich, M.D.
Adjunct Professor of Cardiology
Diagnostic and Medical Clinic
Mobile, AL